Events
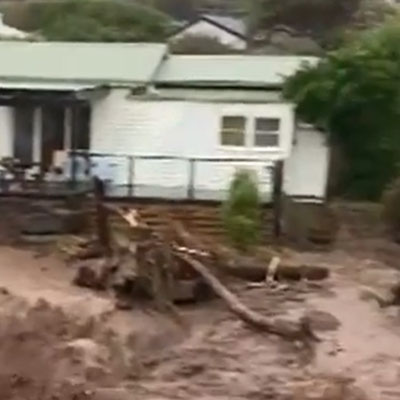
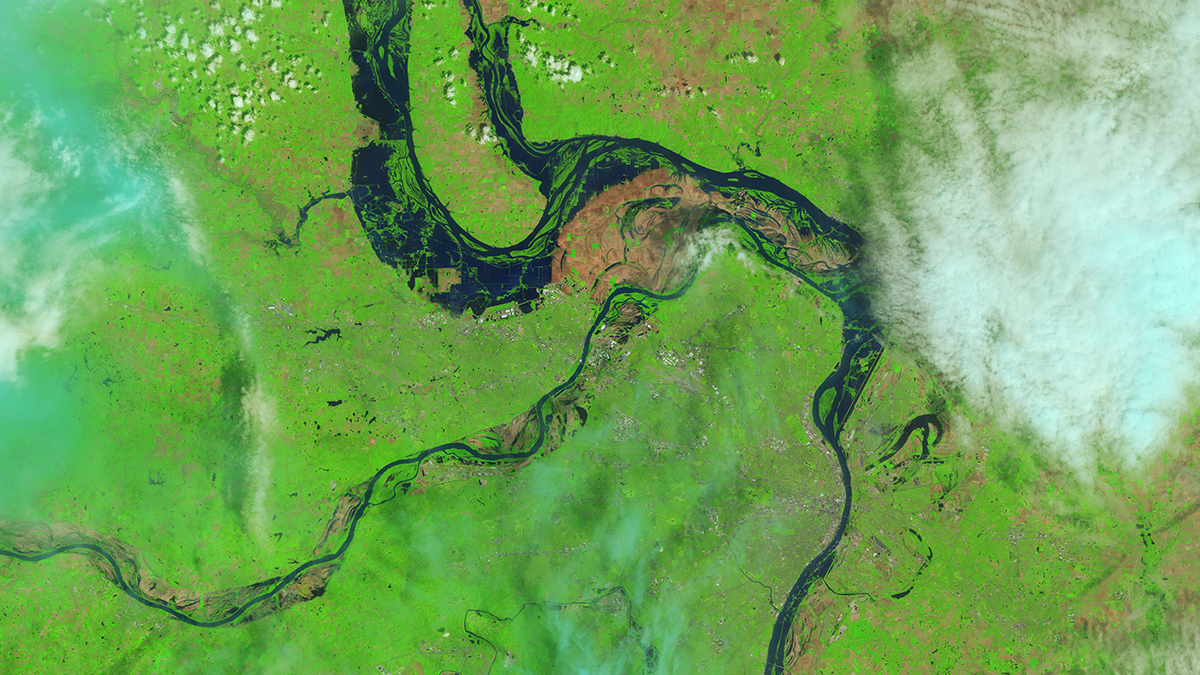
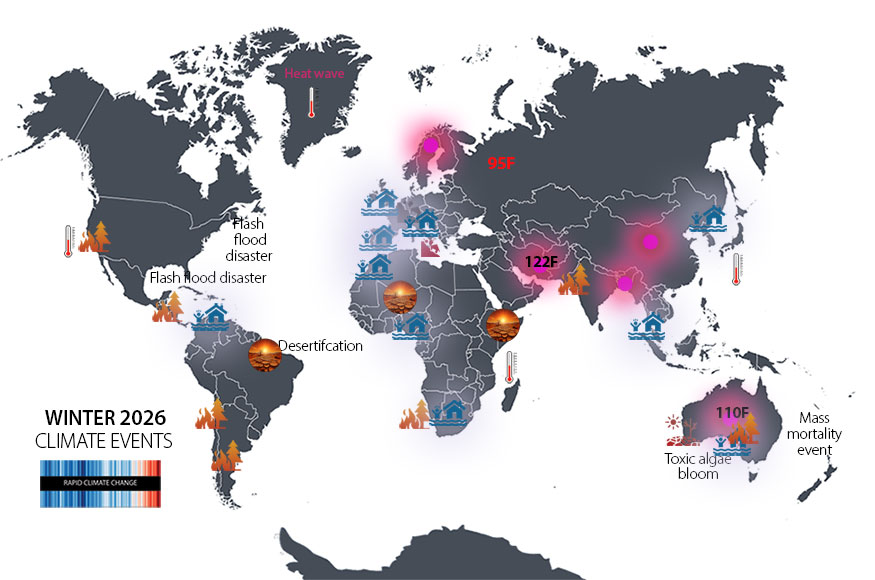
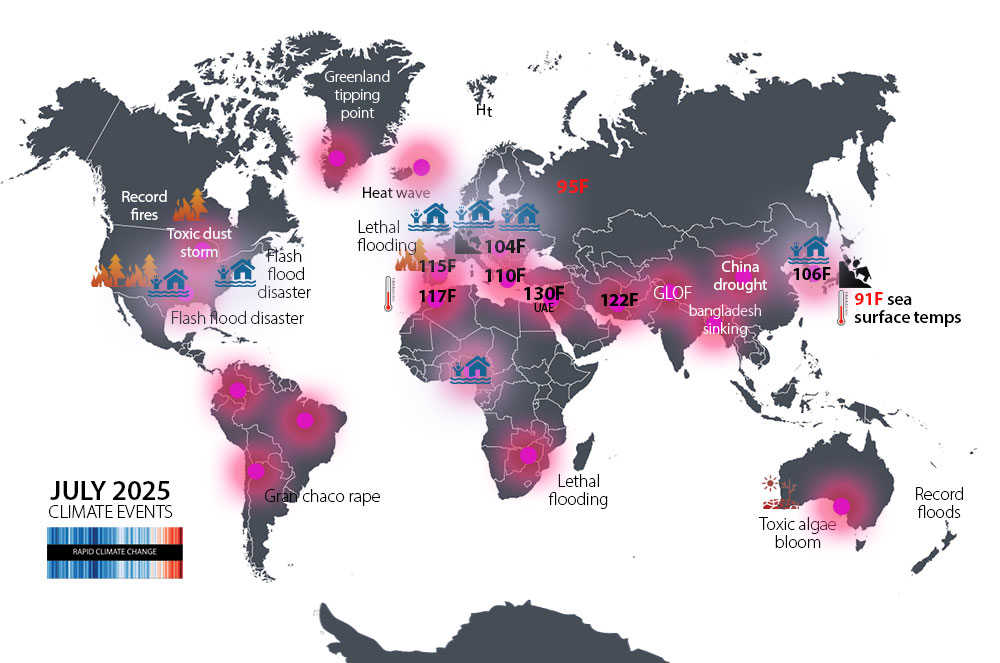
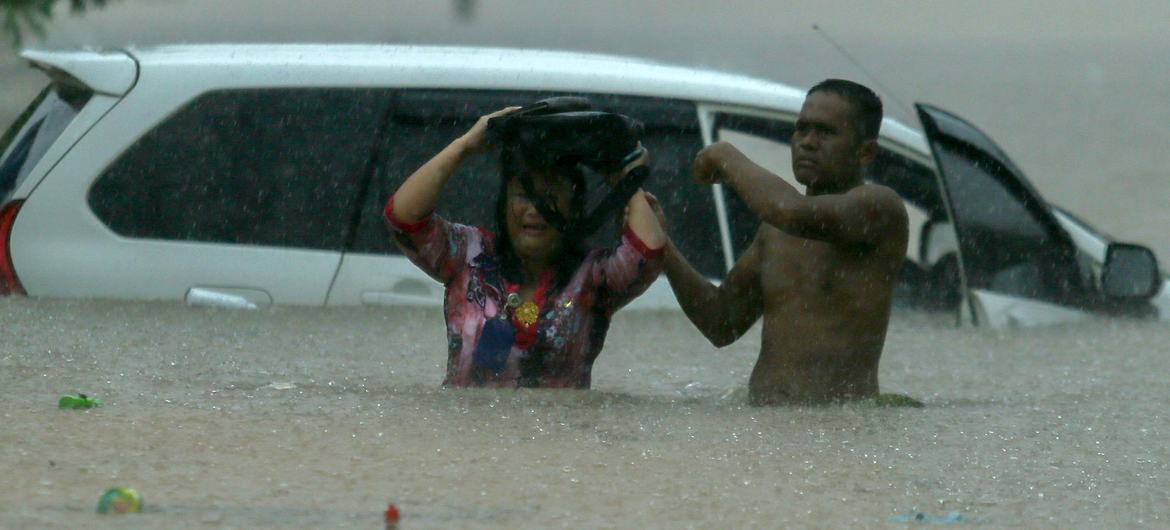
FLOODS/LANDSLIDES: Pakistan (1300), India (1,300), Texas (135), DR Congo (100), Romania (3), Latvia, New Jersey/NY (2), North Carolina, China, Nepal, Korea, UK, Venezuela, Nigeria, Australia.

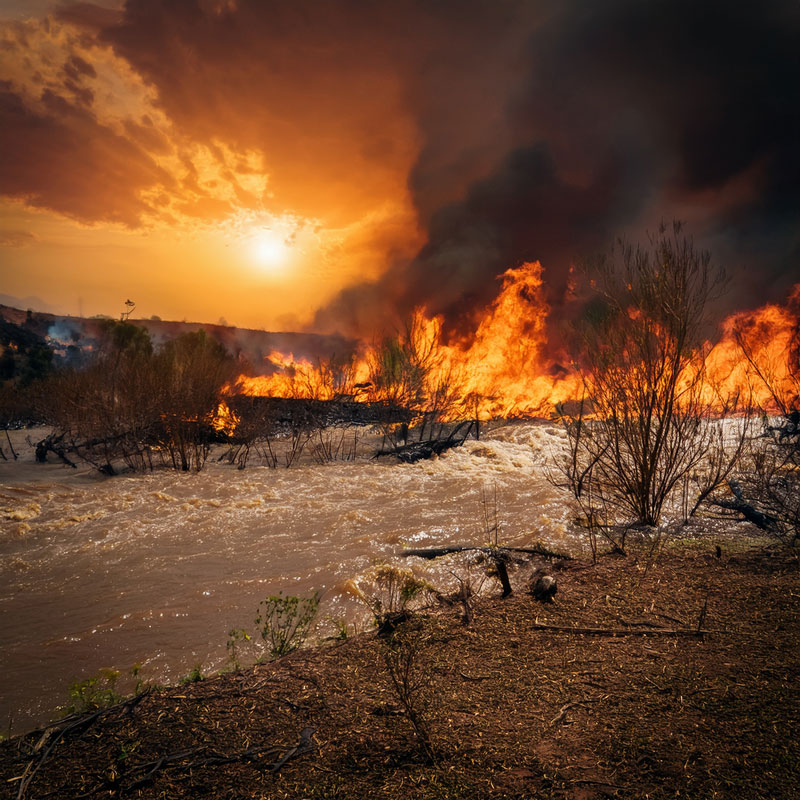
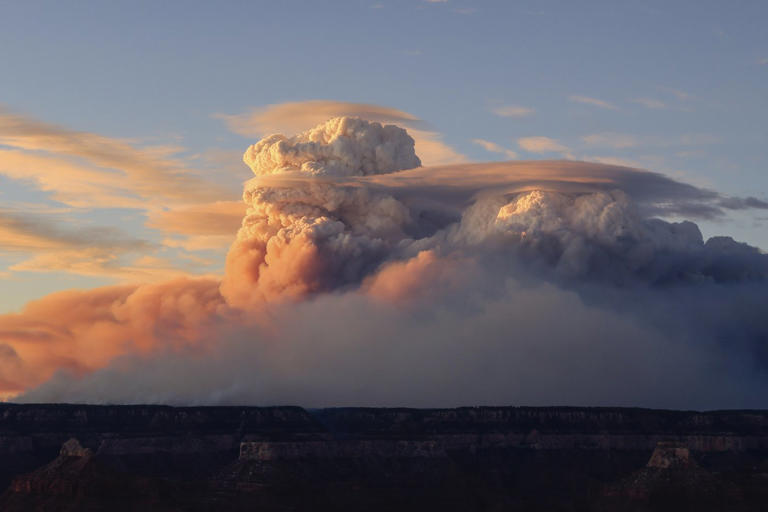
WILDFIRES (1 million Hectares in Europe): Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Spain, Portugal, California, Romania, France, Turkey, Texas, Malaysia, Brazil, Afghanistan, East Africa, Iran, Gran Chaco. In the western US, “fire clouds” produced mini climates. Read more.

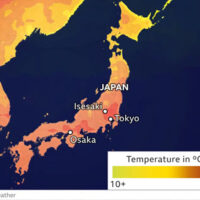
RECORD HEATWAVES: The summers of 2023, 2024 and 2025 were the three hottest on record. The number of lethal heat waves continues to increase. Climate change likely tripled the number of heat-related deaths in European cities. All time records in Japan. Portugal 115F.
INVASIVE TOXIC ALGAE (AU): Since March, a deadly 2,000 sq mi invasion of toxic algae has fouled Australia’s southern coast killing tens of thousands of marine animals and creating an unprecedented ecological disaster.
ANOTHER GLACIER “FUNERAL” Nepal’s Yala glacier has shrunk 66% over five decades, causing researchers to movie their base camp. In 2019, a ceremony was held for the OkjökullGlacier in Iceland. Yala has another decade.
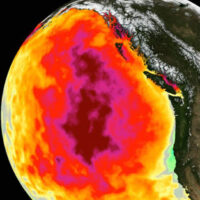
RECORD PACIFIC WARM BLOB The giant pool of record warm ocean water in the north Pacific Ocean is currently showing temperatures averaging 68°F, a degree warmer than the previous record set 12 years ago.
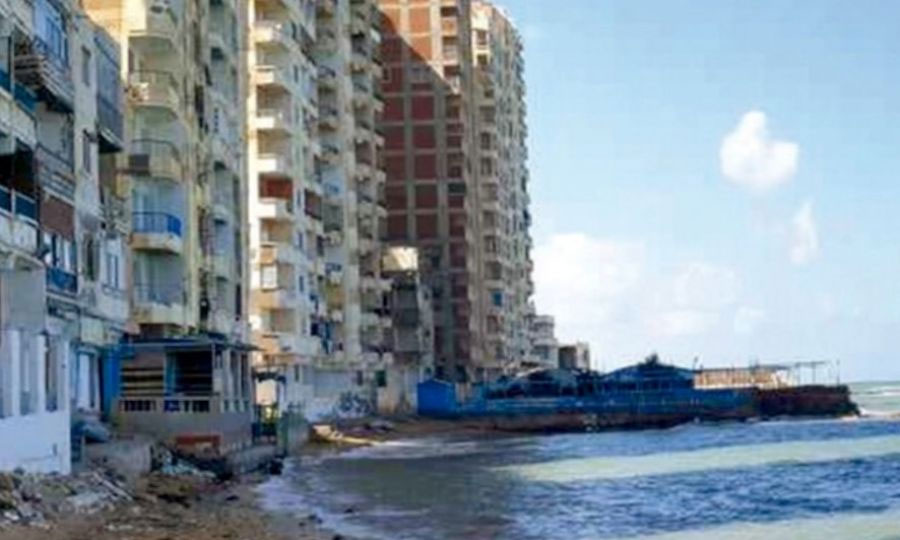
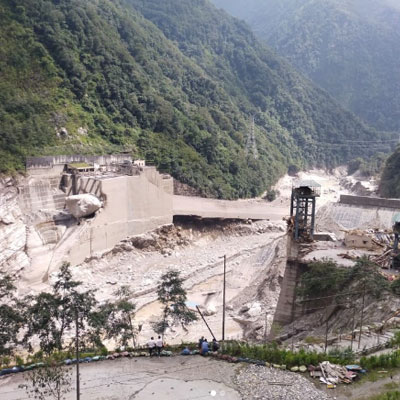
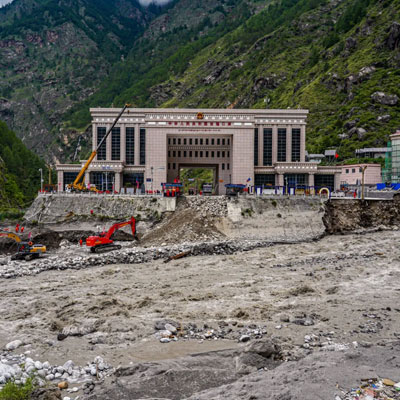
LETHAL GLACIAL OUTBURST FLOOD NEPAL: Another GLOF hit the Himalayan country of Nepal, sweeping away hydropower plants, bridges and other critical infrastructure, killing dozens. Also in Afghanistan and Pakistan.
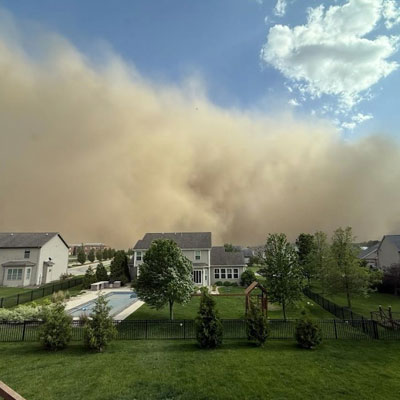
MASSIVE TOXIC DUST STORM HITS CHICAGO A near apocalyptic soil and sand storm developed in central Illinois and moved quickly north to choke the Chicago metropolitan area. Visibility dropped to 0 and winds gusted over 60 mph within the worst of the dust storm. More context here.

:

Trends
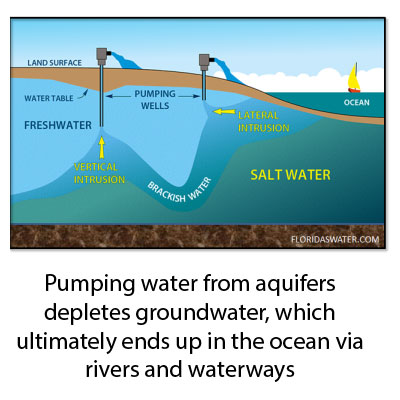
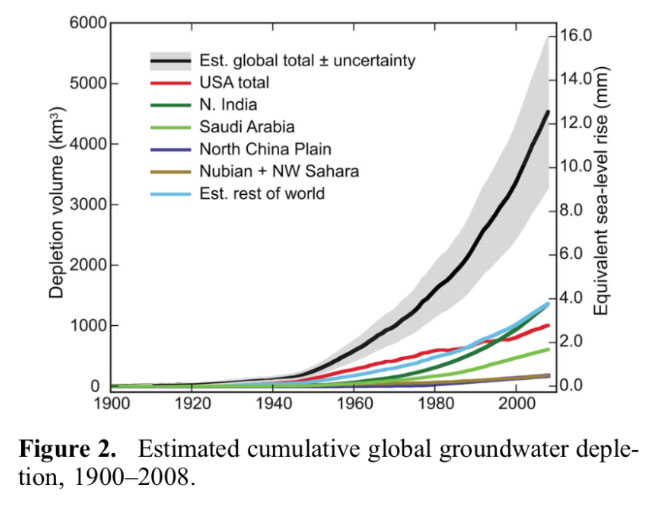
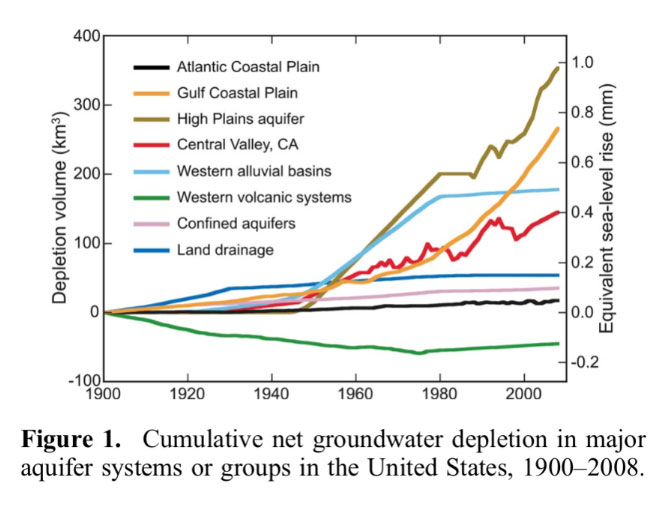
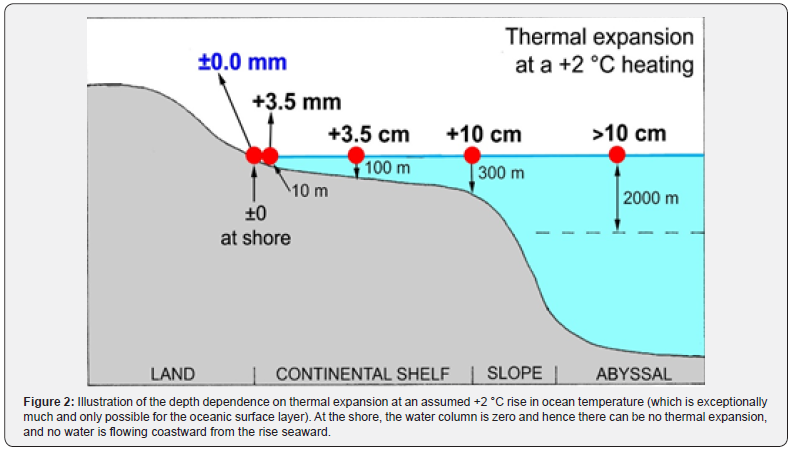
SEA LEVELS: In addition to melting land ice and ocean volume heat expansion, rapid aquifer depletion also contributes about 20% as most extracted groundwater ends up in the ocean. Read more here.
GLACIAL OUTBURST FLOODS INCREASE GLOBALLY: A GLOF occurs in Alpine regions when a rapidly melting glacier creates a high altitude lake behind a moraine dam. When the dam breaks, everything downstream is swept away.
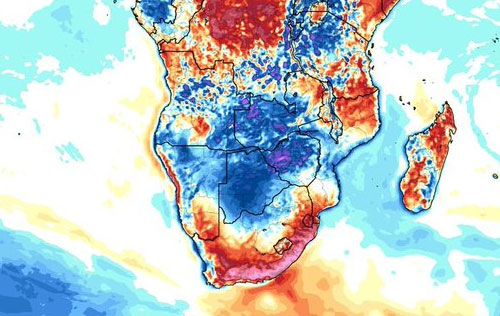
EXTENDED DROUGHT: Arizona, San Carlos Reservoir, Italy, Spain, Australia. Madagascar, southern and eastern Africa, Amazon Basin. Since the beginning of the 21st century, the frequency and intensity of drought events have increased on all continents. Megadrought persists in the US West, with major consequences yet to come.

ANTARCTICA TRANSFORMATION SPEED UP The Southern Pole and environs is undergoing abrupt and alarming changes.
- Sea ice is shrinking rapidly
- Floating glaciers known as ice shelves are melting faster
- Trillions of tons of land based ice sheets are approaching tipping points
- Vital ocean currents are slowing down.
These changes are suddenly accelerating and amplifying individual effects.
ANTARCTIC SEAL POPULATION DOWN 50%: Seal population continues precipitous decline as sea ice disappears. Read more.
CO2 RELENTLESS RISE: As the Trumpies prepare to shut down the world’s preeminent atmospheric carbon measurement station at Mauna Loa, the greenhouse gas of record has climbed past 428 PPM. It first crossed 365 in 2002.
OCEAN TEMPERATURE: Global sea surface temperatures have remained at near-record levels in 2025 following a record-shattering jump in 2023 and 2024.
RETREAT OF GLACIERS AND MORE GLOF: Glaciers are collapsing virtually everywhere around the world. Poorly understood is that they provide fresh water for billions of people in Asia and South America.
DOUBLING OF MAJOR US DUST STORMS Arizona, California, Texas and Kansas have experienced more than 100 dangerous storms in ten years, double the previous count. Bare cropland and rising temperatures are contributing factors.

STINKY SARGASSUM BELT NOW STRETCHES 6000 MILES: While Sargassum seaweed plumes are not new, the floating monster now known as Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt (GASB) is. Driven by warming waters and industrial scale ag nutrients, the brown smelly belt stretches from Africa to the Gulf of Mexico.

Science
TIPPING POINTS: Irreversible feedback loops virtually assure that we are already well past the point of no return. Review major feedback factors here.
1.5°C (2.7F) “THRESHOLD” IN THE REARVIEW: 2025 will be the second year running global temperatures have exceeded the arbitrary limit beyond which humanity dare not go.

NEW SOURCE OF SEA LEVEL RISE: In addition to melting land ice and ocean volume heat expansion, the rapid depletion of groundwater also contributes about 20% as most ends up in the ocean. Read more here.
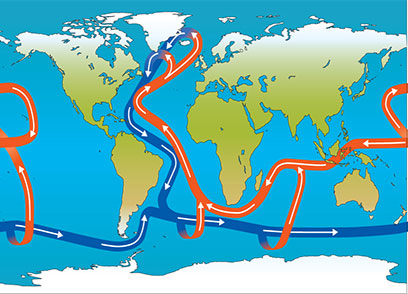
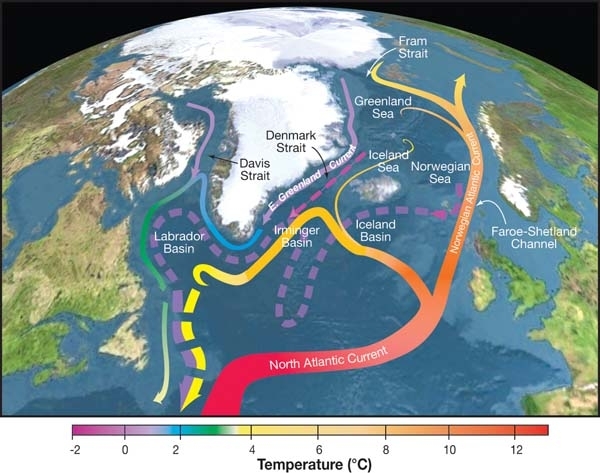
AOMC NOW SLOWING: The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is now weaker than at any other time in the past 1,000 years. The global current moderates temperatures globally and includes the Gulf Stream.
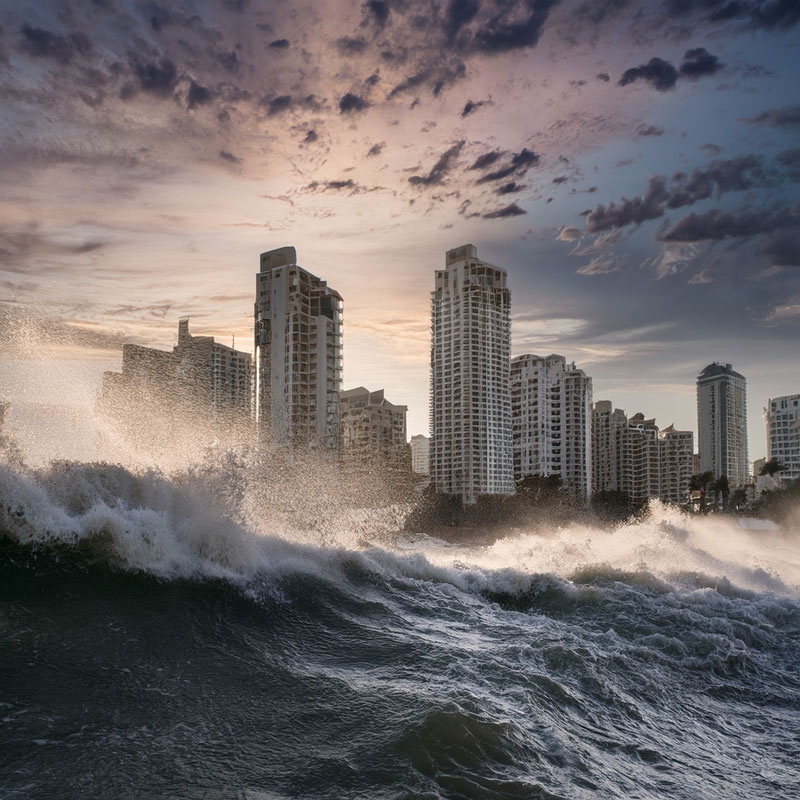
CLIMATE WHIPLASH IS AUSTRALIA’S FUTURE A new scientific risk assessment affirms that Australia is undergoing extreme climate events more frequently and often simultaneously. Extreme recurring temperatures of up to 123°F (winter highs of 107°F) trigger fast moving bushfires, followed immediately by catastrophic floods. Coastal sea level rise is already threatening millions.
GLOBAL INCREASE IN DROUGHTS ALSO BRINGS MORE FLOODS. Extended drought hardens and depletes soils, decreasing the ability of the ground to absorb water. When billions of gallons arrive at once, the deluge swallows everything.
AMAZON TIPPING POINT Global warming has moved the Amazon rainforest to a danger threshold in which the region emits more carbon than it absorbs.
METHANE SPIKE: Atmospheric Methane again reached record-high concentrations. Methane is about 80 times more potent than CO2 over 20 years. Read what happens when the permafrost thaws here.
ICE SHELVES LAST CRITICAL DEFENSE: There is land ice such as that making up most of Antarctica and Greenland, there is sea ice and there are hybrid formations called ice shelves. The latter “hold back” the trillions of tons of ice behind them. They are rapidly falling apart, melting from warming waters below.
HOW RISING TEMPERATURES DRIVE DROUGHT AND EXTREME WEATHER EVENTS : As global temperatures rise, evaporation from land increases, drying plants and soil; simultaneously, water vapor significantly increases in the atmosphere, super charging storms.