When There Is Nowhere Left to Migrate
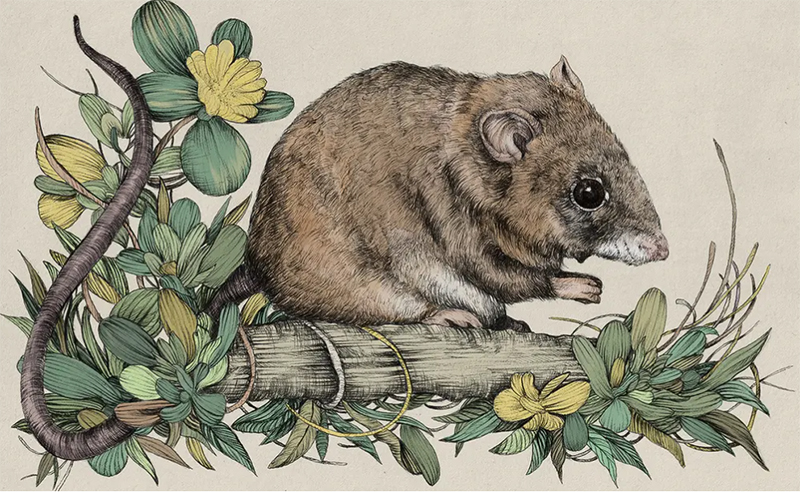
Bramble Cay Melomys (2015)
The first mammal extinction attributed to global warming simply ran out of places to hide.
Rising seas choked the flora on the tiny mammals’ island habitat, and in just a few years they were gone. No one knows how the Bramble Cay melomyses – rodents with large, liquid eyes and reddish-brown fur, small enough to fit in the palms of your hands – ended up on Bramble Cay.
The cay is a very small island about 30 miles off the coast of Papua New Guinea, at the northern end of the Great Barrier Reef. The Melomys and other inhabitants were trapped on the tiny cay, making them vulnerable to every small change in the surrounding ocean. Climate change and rising sea levels led to salt-water intrusions throughout the island, choking much of the flora – in the decade between 2004 and 2014, the volume of leafy plants on Bramble Cay shrank by 97%. Storm surges also winnowed down the population, sweeping animals out to sea.

And Suddenly….
Luxury Food Items
It has long been our belief that Joe Citizen is not going to truly understand what is happening on this planet until their favorite things have gone missing or become so expensive that only the master classes can afford them. See below for likely scenarios.
Wine
Grape harvests threatened in Bordeaux, California and other key wine producing regions are increasinly threatened by steadily warming temperatures.
In California, Scorching temperatures are accelerating evaporation, reducing surface water and drying out soil and vegetation, causing earlier fruit ripening and posing an increasingly dangerous threat to the Sonoma County wine industry.
Salmon
The largest fish farm in New Zealand after a massive die off has closed several of its farms as water temperatures climb into unhealthy ranges for the fish.
“We thought we had more time….”
Shellfish: oysters, clams, mussels and snails
As the ocean absorbs massive quantities of CO2 the waters become more acidic. That is bad in a lot of ways, but one of the most consequential effects is the inability of young shellfish to form their shells. In places like the Gulf of Maine and Puget Sount, they are have been on a downward trajectory for two decades. Beyond the needs of human shellfish lovers, loss of this marine animal segment has cascading effects on the ocean ecosystem.
Species
On land and in the oceans, thee is a general and now ubiquitous movement toward the poles as species attempt to stabilize the habitat their bodies are adapted for. Those that can’t migrate with evolve or disappear.
Insectapocalypse: (Now)
While there is no shortage of ignorant statements made by climate deniers, few can compete with “I hate insects.” I won’t miss them.” Oh, but you will, you really will.
In the case of the startling disappearance of insect populations around the planet, the cause is a combination of climate heating and pesticide abuse, two sides of human destructive behavior on a mass scale.
Hawaiian po’ouli Finch (2005)
Finished off by changes in their habitat, and a myriad of invasive species introduced by humans.
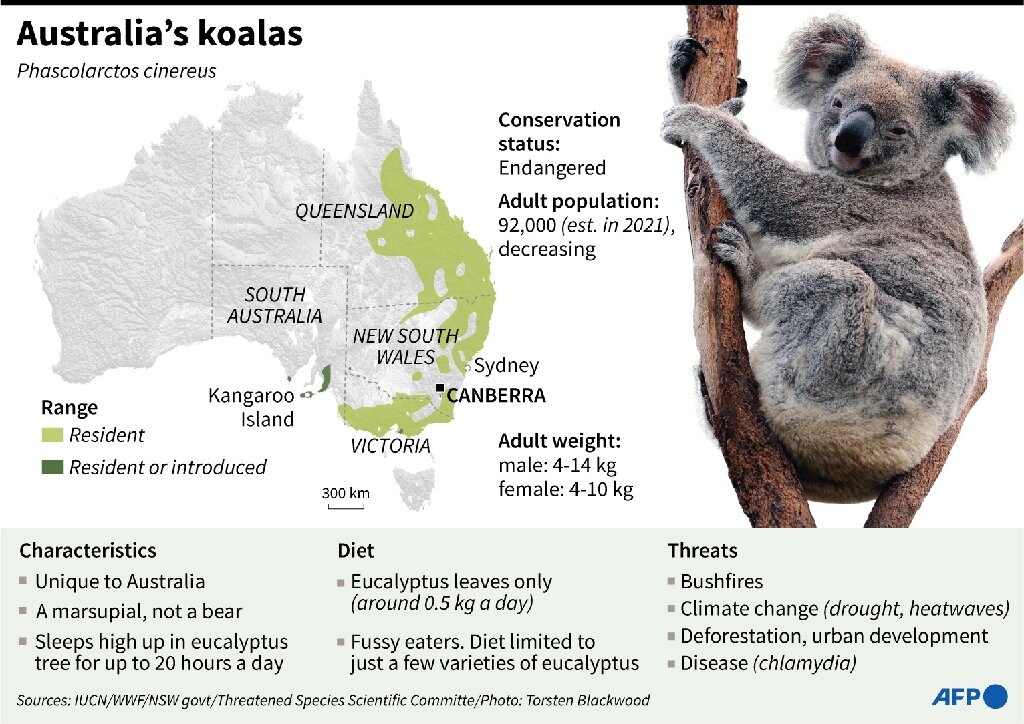
Australia declares koalas endangered
Finished off by changes in their habitat, and a myriad of invasive species introduced by humans.
Elephants Attacking Humans As Habitat Disappears.
The situation is especially dire in Kenya, where heat and an ongoing drought have made thousands of calves orphans.
North Atlantic Right Whales are running out of habitat
Crucially threatened Right Whales are moving into cooler waters as the Gulf of Maine warms alarmingly fast. This exposes them even more to propeller strikes and fishing gear entanglements. Only about 350 animals remain on the planet.
Wild Salmon are getting smaller
The size of Alaskan salmon has declined about 10% in the past 20 years due to warming waters and interaction with farm hatcheries. A new report notes changes in four species: chinook, sockeye, silver and chum..
Places and Refugees
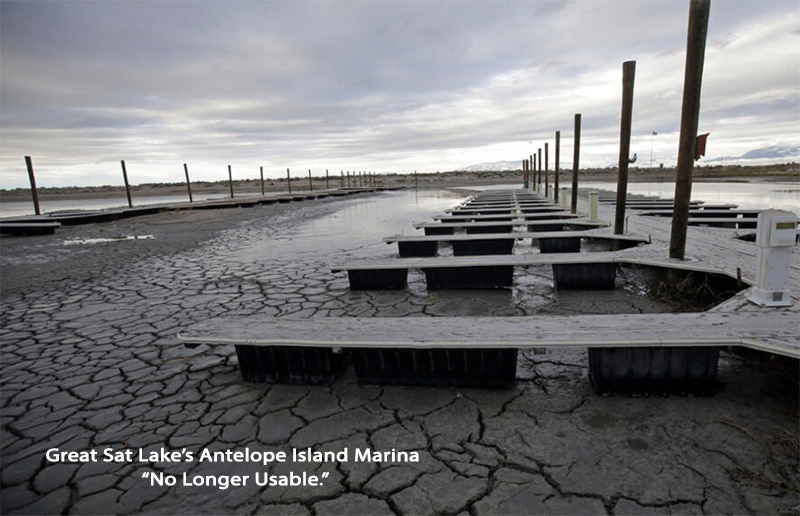
Great Salt Lake Shriveling
The pristine West is more or less a fiction as the quality of water and air continue to degrade. Among the worst regions is around Great Salt Lake, where the surface area of the iconic Mormom watering hole has declined by half. The decline in the lake is attributed to an ongoing drought and stunning misuse of water. About half of the original lakebed area is now dry land. In the process, thousands of square miles of dry lake bed was exposed, laying open vast expanses of arsenic and toxic dust. The situation is initiating a slo mo catastrophic disruption of the food chain.

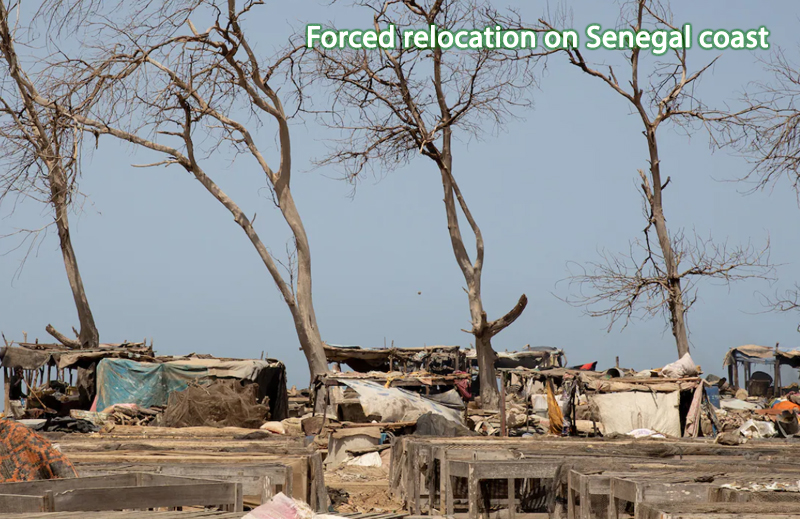
Rapidly rising ocean drives hundreds of thousands from Senegal Coast
In sub-Saharan Africa, up to 86 million people will have to relocate because of climate change by 2050, more than anywhere else on Earth. Thousands in Saint-Louis have already lost their homes or live in what authorities call “extremely high-risk zones.”
80 percent of the city could be underwater by 2080, erasing this world heritage site celebrated for its architecture while uprooting 150,000 people.
Outer Banks, NC (OBX)
OUTER BANKS, NC
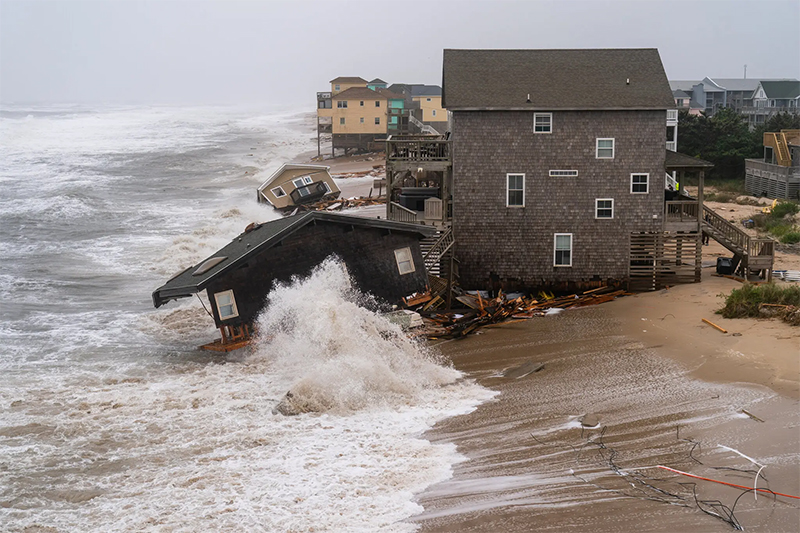

North Carolina’s narrow barrier island vacation land has been under threat from sea level rise for decades, with seas rising approx. one inch every five years. The fact that the islands are prone to massive and sometimes sudden erosion is not news. Global warming is driving ocean encroachment at unprecedented rates, too quickly for sporadic (taxpayer funded) human efforts at containment to have much effect.
San Francisco closing sections of coastal highway
OUTER BANKS, NC

Rapidly rising sea levels are driving San Francisco’s decision to close a mile of the Great Highway – its iconic coastal road – in a high profile move known these days as “managed retreat”. The ocean in this area is expected to rise over 1 foot in the next three decades.
Going, going….







Vanishh